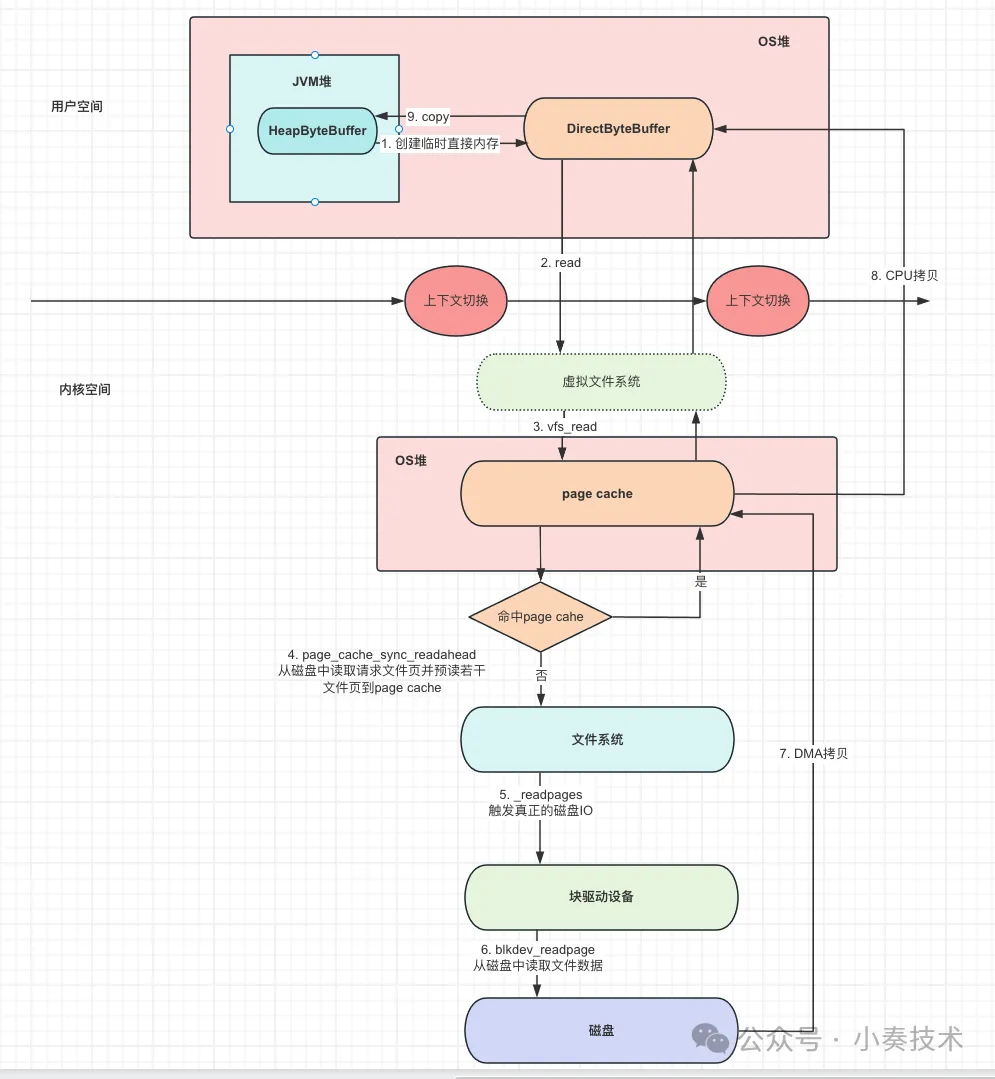
java nio中文件读写不管是普通文件读写,还是基于mmap实现零拷贝,都离不开FileChannel这个类。
随便打开RocketMQ 源码搜索FileChannel。
就可以看到使用频率。
 图片
图片
kafka也是。
 图片
图片
所以在java中文件读写FileChannel尤为重用。
 图片
图片
这里说的仅仅是FileChannel基于堆内存(HeapByteBuffer)的文件读写。
如果是mmap或者堆外内存,可能有些步骤会省略,相当于有一些优化。
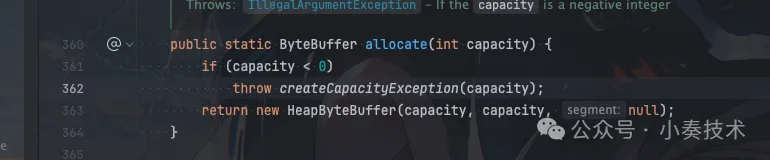
public static void main(String[] args) { String filename = "小奏技术.txt"; String content = "Hello, 小奏技术."; // 写入文件 writeFile(filename, content); // 读取文件 System.out.println("Reading from file:"); readFile(filename); } public static void writeFile(String filename, String content) { // 创建文件对象 File file = new File(filename); // 确保文件存在 if (!file.exists()) { try { boolean created = file.createNewFile(); if (!created) { System.err.println("Unable to create file: " + filename); return; } } catch (Exception e) { System.err.println("An error occurred while creating the file: " + e.getMessage()); return; } } // 使用FileChannel写入文件 try (RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw"); FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel()) { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(content.getBytes().length); buffer.put(content.getBytes()); buffer.flip(); // 切换到读模式 while (buffer.hasRemaining()) { fileChannel.write(buffer); } } catch (Exception e) { System.err.println("An error occurred while writing to the file: " + e.getMessage()); } } public static void readFile(String filename) { // 使用FileChannel读取文件 try (RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(filename, "r"); FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel()) { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) fileChannel.size()); while (fileChannel.read(buffer) > 0) { // Do nothing, just read } // 切换到读模式 buffer.flip(); /* while (buffer.hasRemaining()) { System.out.print((char) buffer.get()); }*/ Charset charset = StandardCharsets.UTF_8; String fileContent = charset.decode(buffer).toString(); System.out.print(fileContent); } catch (Exception e) { System.err.println("An error occurred while reading the file: " + e.getMessage()); } }这里需要注意的一个细节 我们分配的内存的方式是:
ByteBuffer.allocate()这里我们可以进入看看源码:
 图片
图片
实际构造的是HeapByteBuffer,也就是JVM的堆内存。
如果我们使用:
ByteBuffer.allocateDirect()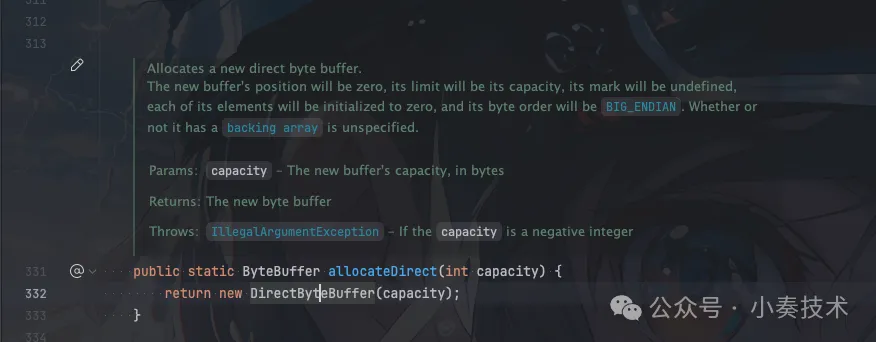 图片
图片
则构造的是堆外内存DirectByteBuffer。
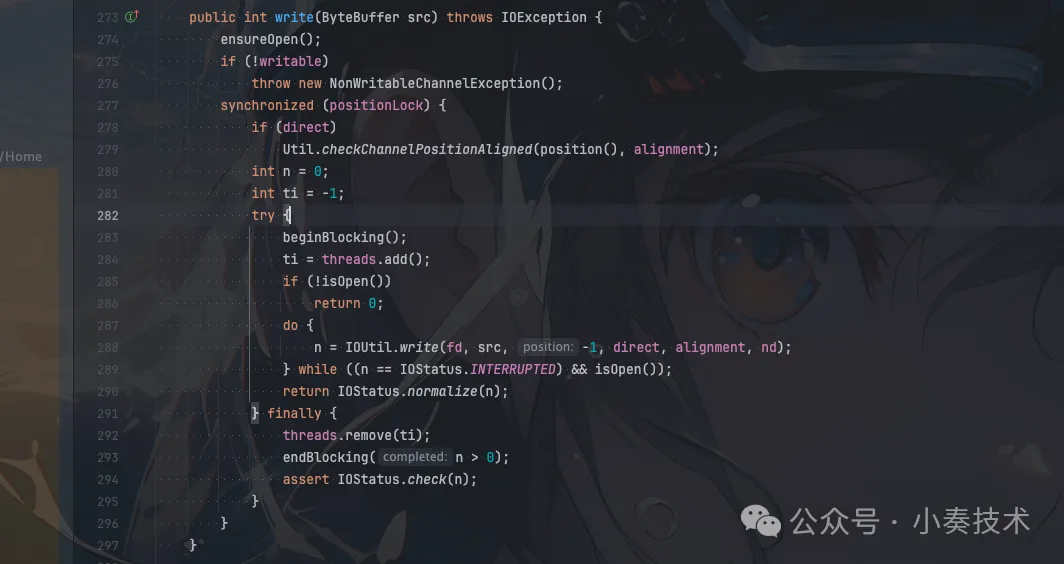
我们看看FileChannel read方法:
 图片
图片
发现IO相关的处理被封装在IOUtil,我们继续看看IOUtil的write方法:
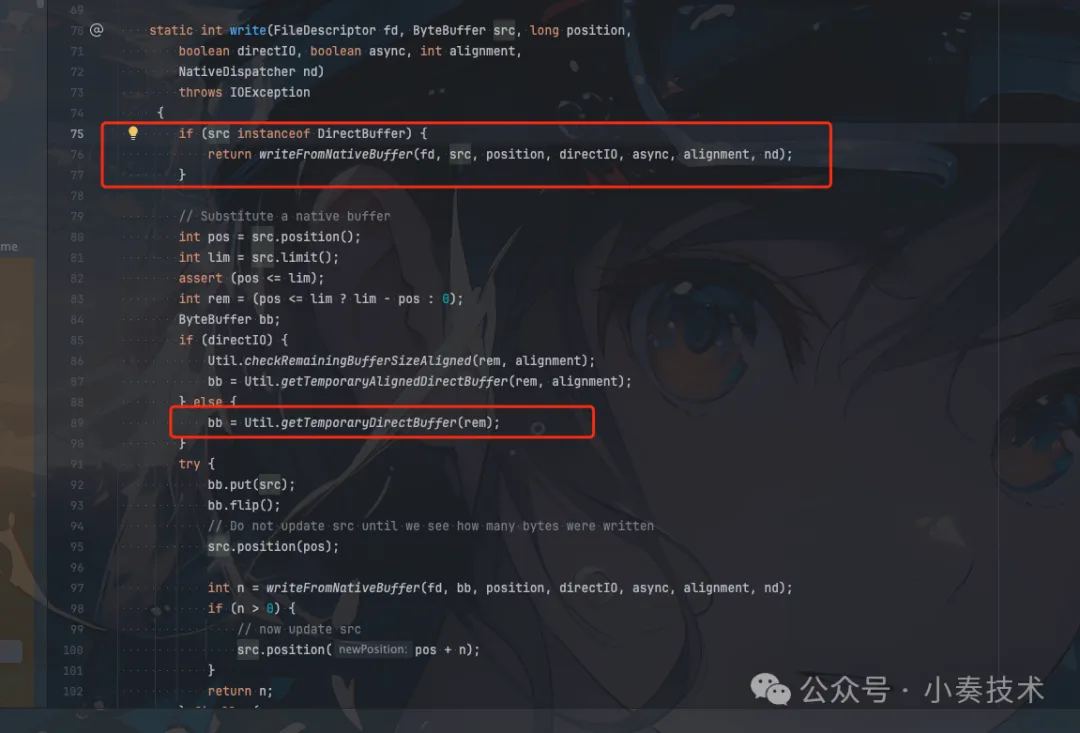 图片
图片
可以看到如果是DirectBuffer则可以直接写。如果是HeapByteBuffer则需要转换为DirectByteBuffer。
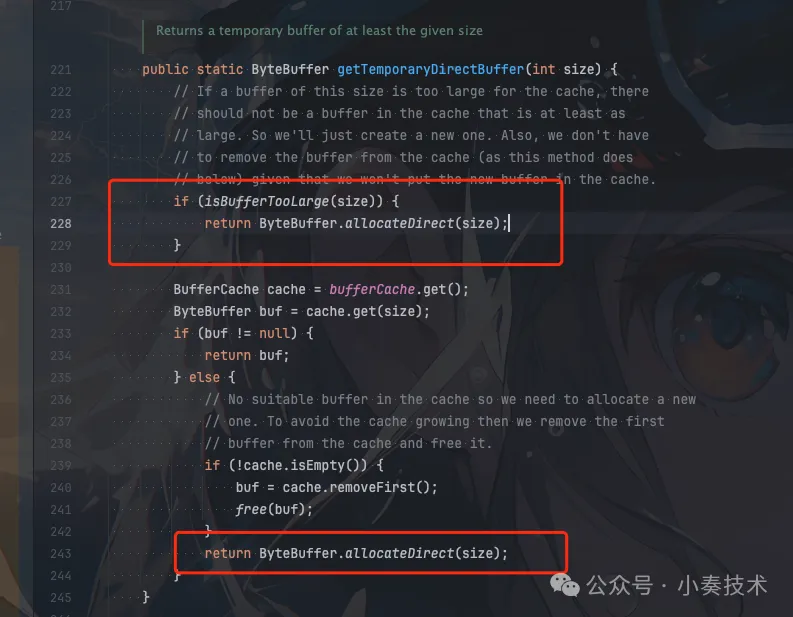 图片
图片
主要是HeapByteBuffer受JVM管理,也就是会受到GC影响。如果在进行native调用的时候发生了GC,会导致HeapByteBuffer的内容出现错误。具体详细的说明可以看看这篇MappedByteBuffer VS FileChannel:从内核层面对比两者的性能差异。讲解的非常清晰。
本文链接://www.dmpip.com//www.dmpip.com/showinfo-26-90858-0.htmlJava Nio FileChannel堆内堆外数据读写全流程分析及使用
声明:本网页内容旨在传播知识,若有侵权等问题请及时与本网联系,我们将在第一时间删除处理。邮件:2376512515@qq.com
上一篇: Wire:Go语言依赖注入的利器