LayoutInflater在Android中是一个非常重要的组件,主要负责将XML布局文件实例化为对应的View对象。LayoutInflater是一个抽象类,不能直接通过new的方式获取其实例,需要通过Activity.getLayoutInflater()或Context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE)来获取与当前Context已经关联且正确配置的标准LayoutInflater。
在实际工作中,有时会根据情况在代码中自定义控件或者加载布局文件,这就需要用到LayoutInflater。它的作用是用来获得布局文件View对象的。例如,在BaseAdapter的getView方法中,LayoutInflater经常被用来获取整个View并返回。
View itemView= LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.layout_list_item,container,false);通过LayoutInflater.from静态函数获得一个LayoutInflater实例,其实是个PhoneLayoutInflater对象:
public static LayoutInflater from(Context context) { LayoutInflater LayoutInflater = (LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE); if (LayoutInflater == null) { throw new AssertionError("LayoutInflater not found."); } return LayoutInflater;}LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE服务跟AMS、WMS等服务不同,完全是APP虚拟的一个服务,主要作用是:在本地为调用者创建PhoneLayoutInflater对象,ContextImpl在注册这个“服务”的时候,将工作委托给PolicyManager,利用makeNewLayoutInflater构建LayoutInflater。
registerService(LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE, new ServiceFetcher() { public Object createService(ContextImpl ctx) { return PolicyManager.makeNewLayoutInflater(ctx.getOuterContext()); }}); public static LayoutInflater makeNewLayoutInflater(Context context) { return sPolicy.makeNewLayoutInflater(context);}PolicyManager进一步调用com.android.internal.policy.impl.Policy对象的makeNewLayoutInflater构建PhoneLayoutInflater。
private static final String POLICY_IMPL_CLASS_NAME ="com.android.internal.policy.impl.Policy";public LayoutInflater makeNewLayoutInflater(Context context) { return new PhoneLayoutInflater(context);}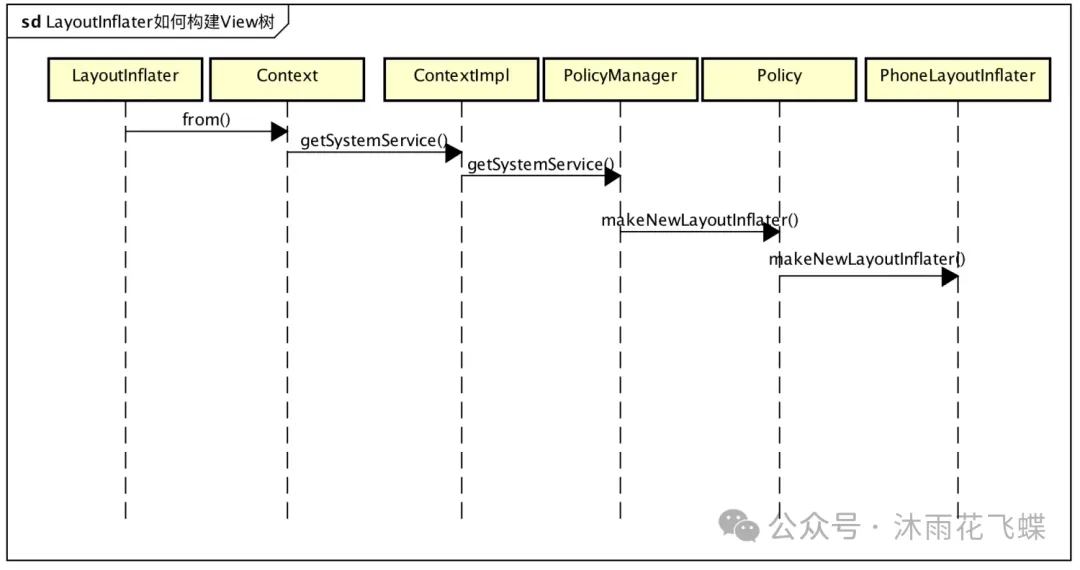 图片
图片
LayoutInflater源码中按照上面的流程来构建View,同时添加了些特殊标签的处理逻辑,比如merge、include、stubview等。
public View inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) { XmlResourceParser parser = getContext().getResources().getLayout(resource); try { return inflate(parser, root, attachToRoot); } finally { parser.close(); }}XmlResourceParser是包含了XML文件信息的一个对象,通过XmlResourceParser将TAG信息取出,递归创建View。
public XmlResourceParser getLayout(int id) throws NotFoundException { return loadXmlResourceParser(id, "layout");}XmlResourceParser loadXmlResourceParser(int id, String type) throws NotFoundException { synchronized (mAccessLock) { TypedValue value = mTmpValue; <!--获取一个TypedValue--> if (value == null) { mTmpValue = value = new TypedValue(); } <!--利用id 查询layout,并填充TypedValue--> getValue(id, value, true); <!--根据布局文件的路径,返回解析xml文件--> if (value.type == TypedValue.TYPE_STRING) { return loadXmlResourceParser(value.string.toString(), id, value.assetCookie, type); } }}TypedValue是与xml定义的资源对应的值,getValue获取对应xml资源:
public void getValue(int id, TypedValue outValue, boolean resolveRefs) throws NotFoundException { boolean found = mAssets.getResourceValue(id, 0, outValue, resolveRefs);}mAssets是一个AssetManager对象:
final boolean getResourceValue(int ident,int density, TypedValue outValue, boolean resolveRefs) { <!--加载资源--> int block = loadResourceValue(ident, (short) density, outValue, resolveRefs); if (block >= 0) { if (outValue.type != TypedValue.TYPE_STRING) { return true; } outValue.string = mStringBlocks[block].get(outValue.data); return true; } return false; }AssetManager通过native函数加载xml文件信息:
static jint android_content_AssetManager_loadResourceValue(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz, jint ident,jshort density,jobject outValue,jboolean resolve){ ...<!--获取native AssetManager对象--> AssetManager* am = assetManagerForJavaObject(env, clazz); <!--获取ResTable资源表,这里应该有缓存 不能每次都弄一次吧? 所有资源的唯一表吗?--> const ResTable& res(am->getResources()); Res_value value; ResTable_config config; uint32_t typeSpecFlags; <!--通过ResTable获取资源--> ssize_t block = res.getResource(ident, &value, false, density, &typeSpecFlags, &config); ... uint32_t ref = ident; if (resolve) { <!--是否需要二次解析资源--> block = res.resolveReference(&value, block, &ref, &typeSpecFlags, &config); ... } return block >= 0 ? copyValue(env, outValue, &res, value, ref, block, typeSpecFlags, &config) : block;}res.getResource并不是是每次都加载一遍,第一次加载后就能获得单例ResTable,后面用的都是这个缓存,只不过ResTable不会缓存全部资源,对于布局、图像资源等,缓存的都是引用,如果是真实资源的引用话,还需要通过res.resolveReference来解析真正的资源。
const ResTable* AssetManager::getResTable(bool required) const{ <!--缓存 ResTable,如果非空直接返回--> ResTable* rt = mResources; if (rt) { return rt; } ...<!--多个apk的话,会有多个--> const size_t N = mAssetPaths.size(); for (size_t i=0; i<N; i++) { Asset* ass = NULL; ResTable* sharedRes = NULL; bool shared = true; <!--找到Asset的路径--> const asset_path& ap = mAssetPaths.itemAt(i); Asset* idmap = openIdmapLocked(ap); <!--这里的路径一般都不是目录--> if (ap.type != kFileTypeDirectory) { if (i == 0) { <!--第一个一般是框架层的系统资源,用的较多,不想每次都解析,需要缓存--> sharedRes = const_cast<AssetManager*>(this)->mZipSet.getZipResourceTable(ap.path); } if (sharedRes == NULL) { ass = const_cast<AssetManager*>(this)->mZipSet.getZipResourceTableAsset(ap.path); if (ass == NULL) { <!--打开resources.arsc文件--> ass = const_cast<AssetManager*>(this)->openNonAssetInPathLocked("resources.arsc", Asset::ACCESS_BUFFER, ap); if (ass != NULL && ass != kExcludedAsset) { ass = const_cast<AssetManager*>(this)->mZipSet.setZipResourceTableAsset(ap.path, ass); }} if (i == 0 && ass != NULL) { <!--缓存第一个asset--> sharedRes = new ResTable(); sharedRes->add(ass, (void*)(i+1), false, idmap); sharedRes = const_cast<AssetManager*>(this)->mZipSet.setZipResourceTable(ap.path, sharedRes); } } } ... if ((ass != NULL || sharedRes != NULL) && ass != kExcludedAsset) { if (rt == NULL) { mResources = rt = new ResTable(); updateResourceParamsLocked(); } if (sharedRes != NULL) { rt->add(sharedRes); } else { rt->add(ass, (void*)(i+1), !shared, idmap); } } .. } return rt;}通过上面的操作,完成了resources.arsc文件的解析,获得了一个ResTable对象,该对象包含了应用程序的全部资源信息(动态加载的先不考虑),之后就可以通过ResTable的getResource来获得指定资源,而对于xml布局文件,这里获得的就是一个引用,需要res.resolveReference二次解析,之后就得到了id对应的资源项。xml布局文件对应的资源项的值是一个字符串,其实是一个布局文件路径,指向一个经过编译的二进制格式保存的xml资源文件。有了这个Xml资源文件的路径之后,会再次通过loadXmlResourceParser来对该Xml资源文件进行解析,从而得到布局文件解析对象XmlResourceParser。
XmlResourceParser loadXmlResourceParser(String file, int id, int assetCookie, String type) throws NotFoundException { if (id != 0) { try {... <!--解析xml文件--> XmlBlock block = mAssets.openXmlBlockAsset(assetCookie, file); if (block != null) { int pos = mLastCachedXmlBlockIndex+1; if (pos >= num) pos = 0; mLastCachedXmlBlockIndex = pos; XmlBlock oldBlock = mCachedXmlBlocks[pos]; if (oldBlock != null) { oldBlock.close(); } <!--缓存--> mCachedXmlBlockIds[pos] = id; mCachedXmlBlocks[pos] = block; <!--返回--> return block.newParser(); ...返回XmlResourceParser对象,进而来实例化各种View:
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) { synchronized (mConstructorArgs) { final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser); Context lastContext = (Context)mConstructorArgs[0]; mConstructorArgs[0] = mContext; View result = root; try { int type; final String name = parser.getName(); <!--Merge标签的根布局不能直接用LayoutInflater进行inflate--> if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) { if (root == null || !attachToRoot) { throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid " + "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true"); } rInflate(parser, root, attrs, false); } else { View temp; if (TAG_1995.equals(name)) { temp = new BlinkLayout(mContext, attrs); } else { <!--利用tag创建View--> temp = createViewFromTag(root, name, attrs); } ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null; if (root != null) { <!--是否有container来辅助,或者添加到container中,或者辅助生成布局参数--> params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs); if (!attachToRoot) { temp.setLayoutParams(params); } } <!--如果有必要,递归生成子View,并添加到temp容器中--> rInflate(parser, temp, attrs, true); <!--是否需要添加到root的container容器总--> if (root != null && attachToRoot) { root.addView(temp, params); } <!--如果不添加root中,返回结果就是infate出的根布局View,否则就是root根布局--> if (root == null || !attachToRoot) { result = temp; } } } return result; }}inflate的主要作用是生成layout的根布局文件,并且根据参数看看是否需要添加container容器中,之后根据需要调用rInflate递归生成子View。
void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, final AttributeSet attrs, boolean finishInflate) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException { final int depth = parser.getDepth(); int type; <!--递归解析--> while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG || parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) { if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) { continue; } final String name = parser.getName(); if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) { parseRequestFocus(parser, parent); } else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) { // inclue标签,不能用在getDepth() == 0 if (parser.getDepth() == 0) { throw new InflateException("<include /> cannot be the root element"); } parseInclude(parser, parent, attrs); } else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) { <!--merge标签必须是布局的根元素,因此merge使用方式一定是被inclue--> throw new InflateException("<merge /> must be the root element"); } else if (TAG_1995.equals(name)) { final View view = new BlinkLayout(mContext, attrs); final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent; final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs); rInflate(parser, view, attrs, true); viewGroup.addView(view, params); } else { <!--创建View,如果有必要,接着递归--> final View view = createViewFromTag(parent, name, attrs); final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent; final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs); rInflate(parser, view, attrs, true); <!--添加View--> viewGroup.addView(view, params); } } if (finishInflate) parent.onFinishInflate();}rInflate主要作用是开启递归遍历,生成View树,createViewFromTag的主要作用是利用反射生成View对象,最终将View数显示到屏幕上。
本文链接://www.dmpip.com//www.dmpip.com/showinfo-26-86982-0.htmlLayoutInflater的工作原理,从解析XML布局文件到创建Java对象,再到构建View树
声明:本网页内容旨在传播知识,若有侵权等问题请及时与本网联系,我们将在第一时间删除处理。邮件:2376512515@qq.com
上一篇: 基于Spring Boot 3.x与Flowable的顺序会签模式实践
下一篇: @Async注解失效的 9 种场景